Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells under a Microscope - MINOR IN BSc BIOTECHNOLOGY (HNRS)
Experiment No: 1
Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells under a
Microscope
Objective:
To
observe and compare the structural differences between prokaryotic and
eukaryotic cells under a light microscope.
Materials:
- Light microscope
- Prepared slides of prokaryotic
cells (e.g., Escherichia coli or Bacillus species)
- Prepared slides of eukaryotic
cells (e.g., onion cells for plant cells, human cheek cells for animal
cells)
- Methylene blue or iodine stain
(optional for staining eukaryotic cells)
- Immersion oil (for high
magnification observation)
- Microscope slides and cover
slips (if preparing fresh samples)
- Droppers and distilled water
(if preparing fresh samples)
Procedure:
- Preparation of Slides:
o Prokaryotic Cells:
§ If using prepared slides, place the
slide on the microscope stage.
§ If preparing fresh slides, place a
drop of bacterial culture on a clean microscope slide, smear it, and allow it
to air dry. Heat-fix the slide by passing it briefly through a flame, then
apply a drop of stain (e.g., crystal violet) if needed. Rinse gently with water
and place a cover slip over the sample.
o Eukaryotic Cells:
§ For onion cells, peel a thin layer
from an onion and place it on a slide. Add a drop of iodine stain, cover with a
cover slip, and avoid air bubbles.
§ For cheek cells, gently scrape the
inside of your cheek with a clean cotton swab and smear it on a slide. Add a
drop of methylene blue stain, cover with a cover slip.
- Microscope Observation:
o Low Magnification (4x or 10x):
§ Start by observing the slide at low
magnification to locate the cells.
§ Identify the general shape and
arrangement of the cells on the slide.
o Higher Magnification (40x or 100x
with immersion oil):
§ Increase the magnification to
observe the detailed structures of the cells.
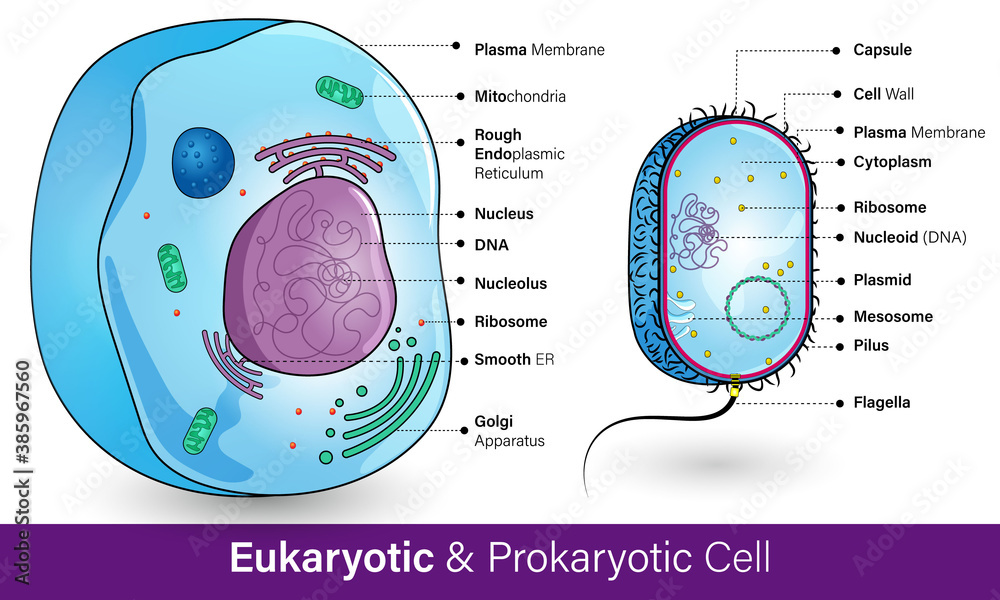
§ For prokaryotic cells, focus on
identifying the cell shape, cell wall, and nucleoid region.
§ For eukaryotic cells, observe the
nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, and, if visible, other organelles like
chloroplasts (in plant cells) or mitochondria.
- Comparison:
o Note the size difference between
prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
o Observe the presence or absence of a
defined nucleus.
o Identify and compare the internal
structures and overall complexity of the cells.
Conclusion:
Prokaryotic
cells are smaller and simpler, lacking a defined nucleus and membrane-bound
organelles, while eukaryotic cells are larger, with a distinct nucleus and a
variety of organelles. This experiment highlights the fundamental structural
differences between these two cell types.
Precautions:
·
Handle
the microscope with care and start with the lowest magnification.
·
Ensure
slides are clean and free of dust or fingerprints.
·
Stain
cells properly to enhance visibility, but avoid overstaining.
·
Use
immersion oil only with the appropriate objective lens and clean it off after
use.
This
experiment provides a visual understanding of the differences between
prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, which are crucial for understanding the
diversity of life at the cellular level.
Observations (Left Side):
|
Feature |
Prokaryotic Cells (e.g., Bacteria) |
Eukaryotic Cells (e.g., Onion or Cheek Cells) |
|
Size |
Smaller
(0.1-5 micrometers) |
Larger
(10-100 micrometers) |
|
Nucleus |
Absent |
Present
(well-defined) |
|
Cell
Wall |
Present
(peptidoglycan in bacteria) |
Present
in plant cells (cellulose); absent in animal cells |
|
Organelles |
None
(no membrane-bound organelles) |
Present
(e.g., mitochondria, chloroplasts) |
|
Ribosomes |
Smaller
(70S) |
Larger
(80S) |
|
Shape |
Simple
shapes (rod, spiral, spherical) |
Varied
shapes depending on cell type |

Comments
Post a Comment